Direct hotspot temperature monitoring compared with other monitoring solutions
January 21 2021
Direct hotspot temperature monitoring compared with other monitoring solutions
Users face several challenges in choosing the right transformer monitoring system (TMS). Each TMS has advantages and disadvantages that users must know when deciding what to specify. Following is a brief summary of the differences between parts of TMS solutions currently available on the market.
DGA
DGA, or dissolved gas analysis, is a well-known condition assessment technology for power transformers. The idea behind it is that applied energy separates gases from the hydrocarbon chain of the transformer oil and dissolves them in that oil. Based on the correlation of different gases, an evaluation can be done to find out which applied energy caused them to emerge.
A DGA monitoring system measures the concentration of gases by volume. Different methods are used to interpret potential failures, the Duval Triangle being one of the most common. The results can provide different failure possibilities in the transformer with a tolerance between 15% and 30%.
Advantages of DGA
Following are the advantages of DGA technology:
- Any transformer can be equipped with a DGA monitor. One can be installed on new transformers and those already in use.
- DGA technology covers a wide range of transformer faults and is often compared to taking blood to determine a person’s state of health.
Disadvantages of DGA
Following are the disadvantages of DGA technology:
- Interpreting the results is difficult and often not clear.
- Highly skilled engineers are required for reasonable interpretation.
- It is difficult to determine next steps, e.g., switch the transformer off and lose money or see if it can run more days or months or even years.
- The DGA method estimates faults only. There is never a clearly measured result.
- Often other parameters, such as transformer temperature, are needed for proper interpretation.
- Ultimately most users take a probe and send it to the oil lab. So why purchase a DGA monitor if a lab is used anyway?
- A DGA monitor can be expensive. Prices range from $5,000 for cheap, single-gas devices to $50,000 for nine-gas devices. DGA monitors with more than nine gases are rarely used.
- DGA monitors cannot be installed and used for the whole lifetime of a transformer. Depending on the DGA technology, periodic calibrations or exchanges of calibration gases and carrying gases are needed. This creates additional constraints and additional costs for the user.
PD monitoring
Partial discharge (PD) monitoring is another way to monitor the condition of a transformer. Two main technologies exist on the market to monitor PD:
- Electrical PD monitoring, which measures each PD in pC.
- Ultra high frequency (UHF) technology, which detects the UHFs of each PD in an insulation medium.
UHF technology is mostly used for PD monitoring in power transformers. The sensors in such cases can be:
- HFCT sensors for use in cable terminations
- UHF drain valve sensor inserted into the drain valve of the transformer
- UHF plate sensors built into the tank wall of the transformer
Advantages of PD monitoring
The advantages of PD monitoring technology are as follows:
- Early fault indication of the insulation material in a transformer is the biggest advantage. The PD monitor indicates insulation faults before they become critical.
- It can be installed on new and older transformers (except the UHF plate).
Disadvantages of PD monitoring
The disadvantages of PD monitoring technology are as follows:
- The whole system is very costly, with prices ranging €10,000 for a very simple configuration to €50,000 for more complex ones.
- As with other technologies, interpreting detected results is a huge challenge. After too many fault alarms, customers start to ignore them, making the whole installation less useful and ultimately a bad investment.
- Cross alarms occur when PD from other assets in the substation (e.g., switchgears or CBs) create PD signals that are detected by the PD monitor installed on the transformer.
Transformer bushing monitoring
Bushing monitors measure the leakage current of transformer bushings. Some monitors on the market can also measure the power factor of the transformer. Such monitors can help indicate faulty bushings on a transformer before they go out of service or even explode.
Advantages of bushing monitoring
The advantages of bushing monitoring technology are as follows:
- It measures values, making interpretation and alarm setting easier.
- Bushing monitoring devices are not costly. Prices range from €5,000 to €20,000. Of course, everything depends on the final configuration, such as the number of bushings to be monitored.
- It can be installed on new and old transformers.
Disadvantages of bushing monitoring
The disadvantage of bushing monitoring technology is as follows:
- It will mainly monitor the bushings of the transformer. It will not show other failures.
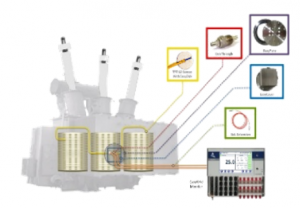 Direct hotspot temperature monitoring
Direct hotspot temperature monitoring
Direct temperature monitoring (DTM) systems measure the temperature in different points in a transformer. Temperature sensors are installed mainly to measure transformer hotspots. More and more users specify sensors to also measure transformer core temperature, oil temperature, and ambient temperature.
Working principle of DTM
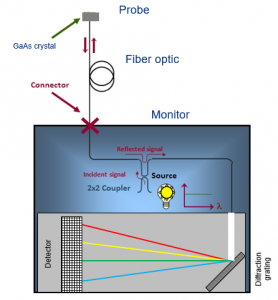
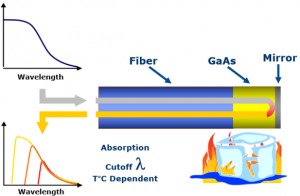 The temperature sensor itself consists of the FO cable, a GaAs crystal, and a mirror at the end. A light source built into the monitor sends a white light to the sensor. The mirror reflects the light and sends it back to the monitor. The GaAs crystal acts as a filter and changes the light wavelength. Therefore the monitor receives a different light wavelength that indicates the exact temperature to an accuracy of +-1°C.
The temperature sensor itself consists of the FO cable, a GaAs crystal, and a mirror at the end. A light source built into the monitor sends a white light to the sensor. The mirror reflects the light and sends it back to the monitor. The GaAs crystal acts as a filter and changes the light wavelength. Therefore the monitor receives a different light wavelength that indicates the exact temperature to an accuracy of +-1°C.
No current is used to measure the temperature, only light. This means the sensor can be installed at any point in a transformer.
Advantages of DTM
The advantages of DTM are as follows:
- Measures the temperature of any point in a transformer.
- Is a real-time temperature measurement, not a calculation or an assumption—just facts.
- No need for an expert to interpret two values, the maximum allowed and the actual measured one.
- Manages transformer load in real time. The dynamic load of transformers is a critical issue with todays’ renewable energies and new governmental regulations.
- Confirms the performance of the transformer during (heat run).
- Does the OEM-provided thermal calculation match the results and specifications?
- Compiles a temperature profile of the transformer.
- Monitors transformer aging and remaining life.
- Has low investment costs and highest ROI compared to other monitoring systems.
Disadvantages of DTM
The disadvantages of DTM are as follows:
- Specifying DTM (brand, number and location of sensors) can be a challenge for users, who should therefore review IEC 60076-2 ANNEX E carefully.
- Most suppliers use still old, less durable 200 μm FO technologies. Only a few suppliers have changed to standard 62.5 μm FO technology. Using older technologies:
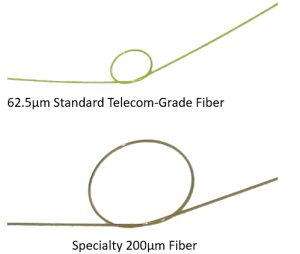
- Reduces the lifetime of the sensor and creates delays in the OEM’s production process
- Creates greater dependence on the manufacturer for non-standard parts
- Can make replacing equipment such as connectors and monitors difficult
- It can be difficult to find suppliers with a long, proven history.
- In most cases, DTM monitors can be installed on new transformers only.
Find out more in the chapter on five things to consider when specifying FO temperature monitoring.
Conclusion
Ultimately, users themselves must decide which TMS delivers the best ROI for their particular case. The table below can help with that decision.

Due to its low cost and easy interpretation, DTM has the highest ROI. This is why DTM is currently the fastest-growing part of TMS. Correctly specifying a DTM system based on the latest technologies (such as a standard 62.5 μm FO cable) and recommendations from IEC 60076-2 ANNEX E is therefore key.



